Economic preferences of children
Project descriptions, links to papers and presentation slides
Drivers of Behavior at an Early Age
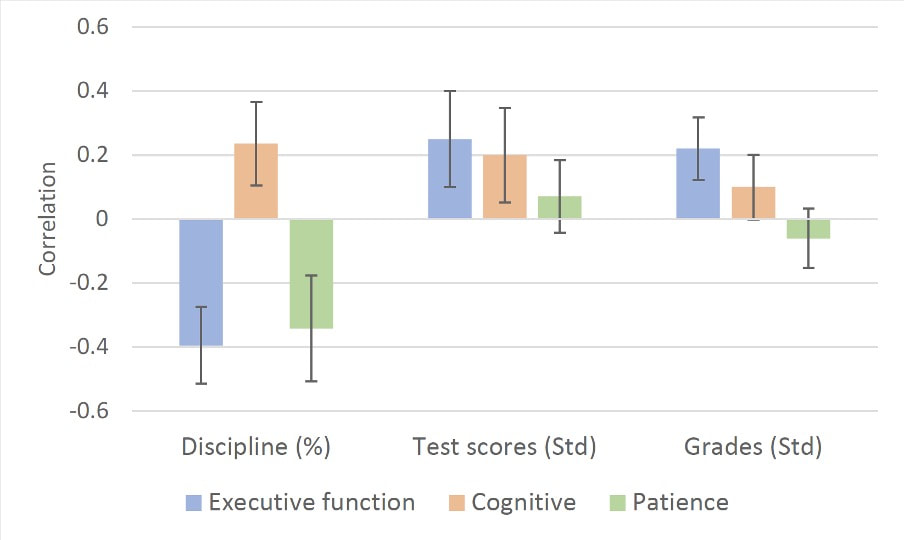
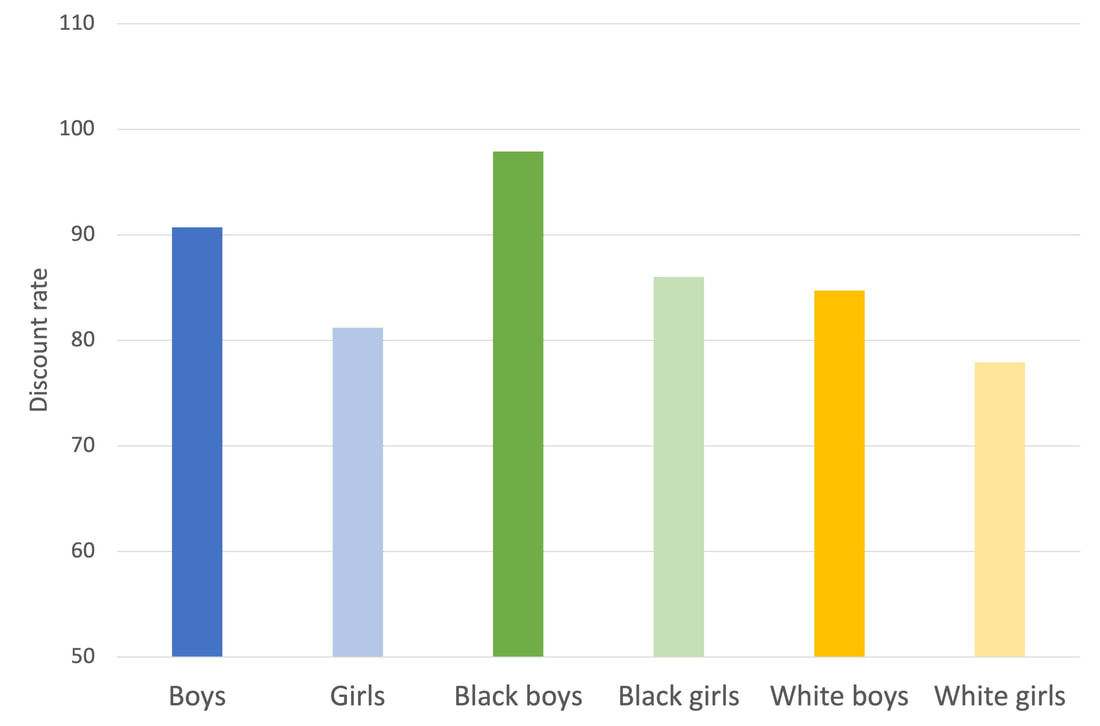
How do the skills developed when children are 3-5 years old drive schooling outcomes in middle childhood and adolescence? Skills map onto three distinct factors - cognitive skills, executive functions, and economic preferences. Executive functions reduce disciplinary referrals, and increase test scores and grades. Cognitive skills increase test scores and weakly reduce disciplinary referrals, but do not predict grades. Economic preferences have an independent effect: children who are patient in early childhood have fewer disciplinary referrals. Finally, random assignment to preschool impacts grades and disciplinary referrals through changes to cognitive skills and executive functions. Link to paper Castillo, Marco, John List, Ragan Petrie and Anya Samek, "Detecting Drivers of Behavior at an Early Age: Evidence from a Longitudinal Field Experiment," forthcoming, Journal of Political Economy. |